Introduction
As lifestyles become more complex and demanding, people often find themselves on the verge of depressive disorders. They are dealing with constant pressure and an inability to cope. Mental illnesses were previously a rare occurrence. Today however, they are widespread and can hinder a person’s ability to function productively. Over time more and more people find themselves withdrawing from normal life.
Depressive disorders are becoming more and more common. While there is no sole root cause, the symptoms are real and act as proof of its existence. Different experiences and endeavors can impact people in a variety of ways; if any of these happen to be particularly traumatic, they have the potential to trigger depressive symptoms.
Clinical depression takes up many forms. More often than not, it is comorbid with other disorders. Hence, diagnosis becomes a jumble of conditions and medical concerns. These conditions can influence a person’s quality of life and physical health negatively. Some may make impulsive and harmful decisions while in their depressive state. Before we dive into the causes, symptoms, and treatments for depression, it’s important to understand the difference between the kinds of depressive disorders.
Types of Clinical Depression
Although there are numerous types of depression, they can be categorized as chronic depressive disorders or within a group of other disorders that are less common. Chronic depression lasts for long periods of time; even after a cheerful experience that uplifts their mood, the individual returns to the original depressive state again.

In the other categories, depressive symptoms subside over time, and usually return in short bursts of depressive episodes and the cause is usually a change; for example, something that the individual hasn’t gotten used to.
Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD)
Also referred to as dysthymia, Persistent Depressive Disorder is a type of chronic depression that affects the individual over the long-term. As one stays in the depressive spiral, they lose any interest they used to have in everyday routine activities, feel a lack of motivation, and as a result, are less productive. This affects self-image and creates one of inadequacy and lower self-esteem. As these feelings continue to cloud the mind, they can hinder progress at the workplace, school, and even in relationships.
According to the DSM-5, the diagnostic criteria for PDD states that children and adolescents should exhibit symptoms for one year, while adults should experience them for two years. Persistent display of symptoms like poor appetite, overeating, insomnia, low energy or poor concentration for a prolonged period is a sign of PDD. The cause is always something subjective since each person responds to an event in a distinct manner; so while some may have inherited the condition from their parents, others have developed it because of traumatic experiences.
Everyone experiences symptoms and responds to treatment methods differently. Treatments for PDD vary from cognitive behavioral therapy, counseling, and medication, with some studies showing favorable results for herbal medicine.

As these [depressive] feelings continue to cloud the mind, they can hinder progress at the workplace, school, and even in relationships.
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
The second form of chronic depression is major depressive disorder (MDD) which has a higher degree of severity than PDD, but it is less chronic as well, meaning individuals experience it intensely but with frequent intervals rather than all the time. Although some symptoms align with those of persistent depressive disorder, they will be much more severe to the extent that the affected person feels that their life ‘isn’t worth living.’ Hence, suicidal thoughts are one way that MDD is different from PDD.
Similar to dysthymia, MDD affects an individual’s daily activities and way of life, but on a severe scale, it negatively impacts their decision-making capabilities. Rather than feeling a loss of interest in even their favorite hobbies, affected people will find themselves constantly consumed by thoughts of hopelessness and emptiness.
Because of their highly depressive thoughts, they make blunders in everyday activities, which leads to guilt and self-hatred. Negative emotions affect the body, which results in unexplained aches; the vicious cycle continues, and thoughts of suicide take control of their mind because they can’t understand why they feel the way they do.
According to DSM-5, to be diagnosed with MDD a person must display five of the following symptoms during a two week period. Of the five symptoms, at least one should be depressed mood or a loss of pleasure in daily activities.

- Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day.
- Noticeably diminished interest or pleasure in all, or mostly all, activities most of the day, nearly every day.
- Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain, or decrease or increase in appetite nearly every day.
- Slowing down of thought and a reduction of physical movement (observable by others, not merely subjective).
- Fatigue or loss of energy nearly every day.
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt nearly every day.
- Diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness, nearly every day.
- Recurrent thoughts of death, recurrent suicidal ideation without a specific plan, or a suicide attempt or a specific plan for committing suicide.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Shorter nights and daylight saving time can also be a cause of distress for some people

A very rare kind of depression, Seasonal Affective Disorder is a type of major depression, except it recurs with a pattern based on seasons. Seasonal affective disorder comprises 1 to 10 percent of all depressive disorders and is more likely to affect women than men. According to the DSM-5, SAD isn’t a depressive disorder on its own that requires a diagnosis of completely different symptoms. It’s simply a recurring form of major depression on a seasonal scale.
However, while the symptoms are similar to those chronic forms of depression, the DSM-5 diagnoses seasonal affective disorder differently. To meet the diagnostic criteria, the individual should experience depression only during a specific time of the year while in other seasons they should exhibit complete remittance. The person should be showing signs of SAD for the last two years consecutively, and there should be a higher count of seasonal depressive episodes than non-seasonal depressive episodes.
The causes for such a disorder vary from person to person, depending upon where they live. For instance, their biological clock may be what is causing depressive symptoms due to less exposure to sunlight. Seasonal changes can reduce the levels of serotonin, a mood-affecting neurotransmitter, in the brain, which leads to depressive mood and symptoms. Shorter nights and daylight saving time can also be a cause of distress for some people, and it eventually transforms into agitation and depressive mood that doesn’t subside.
People who live in a certain area are at a higher risk of developing seasonal affective disorder than people who live somewhere else. For example, SAD also heavily affects people who tend to live farther from the equator because of how daylight levels change drastically in winter.
Postpartum Depression
This depression is different because it affects women after they’ve given birth. Rather than just a range of emotional symptoms, women with postpartum depression experience many physical and behavioral changes due to the effect of a newborn baby. Although depressive symptoms are somewhat the same, the DSM-5 states that this form of major depression occurs within a month after a woman delivers her baby.
However, since postpartum depression is complex, specialists diagnose it differently based on the time difference between the delivery and the onset of depression. It also depends on how severely the woman experiences symptoms.
The cause of postpartum depression is rooted in the various hormonal and physical changes that a woman’s body undergoes during pregnancy and delivery. In addition, the onset can also be because of the new experience of looking after a baby.
When pregnant, a woman’s estrogen and progesterone levels surge up to ten times their regular level but shortly after the delivery; they plummet back to their original level from before pregnancy. Aside from the hormonal changes, a woman feels many social changes and responsibilities after having a baby, which increases her risk of depression.
Symptoms are common aspects associated with having a baby, such as a lack of sleep, feelings of tiredness, a change in appetite and constant changes in mood. The diagnosis depends not on these common postpartum factors, but rather on the occurrence of symptoms like depressed mood, suicidal thoughts, hopelessness, and a loss of pleasure in spending time with her baby.
Other factors like age and number of children further increase the risk of postpartum depression. Fortunately, the wave of depression passes quickly in most women, and during the depressive stage, counseling or medication can help when dealing with symptoms.

A woman feels many social changes and responsibilities after having a baby, which increases her risk of depression
PTSD and Depression
PTSD or posttraumatic stress disorder is different from depression, but it can often co-occur with depressive symptoms. Moreover, PTSD itself is an anxiety disorder that develops after a person witnesses or experiences a traumatic event. In turn, it leaves the person with feelings of anxiety.
The most common examples of people who have PTSD are war veterans. This is because of the traumatizing nature of what they have experienced and witnessed while on the field. PTSD is often comorbid with symptoms like paranoia and completely different neurological disorders like prosopagnosia which is an inability to recognize faces. Studies that researched the effects of war on soldiers found that they would often suffer from both PTSD and prosopagnosia.
Depression and PTSD aren’t the same. However, because of the conditions due to which people develop PTSD (for instance, the loss of a loved one), depression can occur. After losing a close friend or family member, especially someone that the individual would enjoy daily activities with, a person could lose interest in their routine. In severe cases, the person concerned will have suicidal thoughts. Simply put, they feel like ‘life isn’t worth living.’

The symptoms of PTSD include:
- Emotional distress in the form of flashbacks and nightmares
- Physical behaviors like conscious avoidance of reminders
- Anxiety
With depression, they will also experience:
- Mood changes
- Lack of interest
- Feelings of worthlessness
Although both disorders can occur together, psychological specialists diagnose each of them separately according to the DSM-5. The reason for the separate diagnosis is the distinct nature of the conditions.
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar depression was previously diagnosed as manic depression. Brief episodes of mania are the main characteristic of this condition. This mental disorder is distinct because it isn’t chronic, but the depression doesn’t subside over time, either. Instead, instances of abnormally elevated moods separate depressive episodes.
This drastic shift in mood is mania. In some cases, it is hypomania. The presence of symptoms of psychosis differentiates hypomania. The emotional highs and lows that a person experiences can significantly affect their day-to-day behavior. Each state has opposite symptoms. In addition, there is no fixed time when they will transition from a depressive episode to an instance of mania.
Two Types of Bipolar Disorder
There are two main kinds of bipolar disorder; I and II. In bipolar disorder I, the person will experience instances of severe mania and at other times, depression. In bipolar disorder II, the affected person will experience a toned down version of mania, called hypomania.
Similarity between Type I and Type II
Now the similarity between both types of bipolar disorder is the occurrence of major depressive episodes. These will exhibit symptoms of:
- Suicidal thoughts
- No interest in activities that the individual would otherwise enjoy during a manic episode
- Unexplained tearfulness
- Insomnia (or hypersomnia)
Another similarity that both types share is the presence of neutral stages when they experience neither mania nor depression.
Difference between Type I and Type II
Both types are different regarding their respective manic episodes; while type I involves mania, type II involves hypomania. For starters, a complete manic episode will last for a minimum of seven days. During this period, the individual will experience feelings like euphoria, more active and increased libido, and delusions.
Bipolar depression was previously diagnosed as manic depression.
During this period, an affected individual will be prone to engaging in risky behavior. Moreover, he or she makes decisions impulsively when it comes to spending money or handling relationships. However, a manic episode doesn’t mean that the individual will become coherently violent – this is a myth.
On the other hand, similar symptoms indicate a hypomanic episode. The difference is that they won’t be functioning impulsively. They will enjoy the better mood and increased energy. However, they won’t engage in reckless behavior that could result in injury, to them or someone else.
There are no exact causes that can lead to the development of bipolar disorder. However, some factors, like genetics and societal conditions, can influence the person and put them at risk.
Nearly 15% of the general population will experience clinical depression over the course of their life.
Causes
Depression is one of the most complex mental disorders known to man. There are multiple causes of depression. Moreover, its presence can prohibit people from functioning properly. Since many now recognize depression as a concerning health issue, people often look for its cause. Unfortunately, there is no single cause for depression and different things can trigger it.
From poor nutrition and diet imbalance to brain chemistry imbalance and physical health problems, there are many factors that can lead to depression. However, experts have found that genetics, anxiety, grief, and changes in life are frequently culprits that contribute to depression.
Genetics
Genetics is one of the major causes of depression. Nearly 15% of the general population will experience clinical depression over the course of their life. People who have relatives that suffer from depression are nearly five times as likely to be a victim of clinical depression. With the help of adoption studies as well as twin and family studies, experts have been able to determine whether genetics are truly a major cause of depression.
Through twin and family studies, experts at the World Health Organization have been able to confirm that blood relatives of a clinically depressed patient are nearly 40% to 50% at a higher risk of being clinically depressed at some point of their life. Most of the researchers and experts used different techniques. These techniques include twin studies and linkage studies, which give the most promising results. Bipolar disorder is also a significant benefactor to genetically induced depression.
Finding the genetic risk of depression is very hard for researchers due to the many mental disorders that exist. Researchers looking for a single symptom of depression in genetics might find multiple disorders within one person. This limits the possibilities for finding a genetic link for depression and how it runs in the family.
So far, researchers have yet to find any specific gene that can cause depression among family members. Moreover, the average number of people suffering from depression is rising significantly. However, there is no significant change in genetics. This factor leads experts to believe that genetics is only a small piece of what is a huge puzzle.

Anxiety
Anxiety is not just a single medical disorder; instead, it is a culmination of multiple disorders that can physically and mentally affect a person. Since people suffering from different types of anxiety such as obsessive-compulsive disorder or social anxiety disorder often stay agitated, this agitation can take a severe emotional toll on these people. This emotional toll is what gives way to depression. Moreover, this is the reason why many people suffering from anxiety also suffer from depression.
Anxiety itself is one of the most complicated mental disorders of this generation. Again, the reason is that there are multiple possible causes of anxiety. Contrary to popular belief, anxiety is a lot more than just worrying and stress. People suffering from anxiety can be afraid of things or situations that other people wouldn’t even consider. Even if they know it may be foolish, they cannot seem to stop themselves from thinking about it. When people become anxious they tend to have pervasive thoughts about some worry or problem and then feel bad about it. This can lead to feeling like a failure which can then move into depression.
While depression and anxiety are two very different types of mental disorders, patients suffering from depression often suffer from anxiety as well. People who are often depressed begin to feel worried and anxious, which further indicates that one of these disorders can activate the other.
Though these two disorders can activate each other, anxiety often comes before depression. Moreover, rarely does depression lead to anxiety. That said, people who have PTSD are the most likely to suffer from depression. The incidence is greater when compared to other forms of anxiety.
With clear evidence that anxiety can potentially cause depression, people who have family members that suffer from any form of anxiety are also at risk of getting depression. Most mental disorders pass down from generation to generation and anxiety is one of them, which makes it possible for people born with anxiety to also be depressed, and vice versa.

[People] suffering from depression often suffer from anxiety as well.
Grief
Grief is something that everyone suffers from throughout their life making it one of the most common experiences that people share. Whether it be from losing a loved one, a job, or a house, most people will experience a period of grief during their life. The real problem is when grief slowly begins to morph into depression. This occurrence is quite common. To understand how this happens one must understand the difference between the different mental disorders. One must also understand prolonged grief and depression, and how these two interconnect.
Grief and depression are two very different disorders but have similar symptoms. More often than not doctors categorize people who are in grief as clinically depressed, which can be inaccurate. Losing a loved one is a very personal and gut-wrenching experience, an experience that no one can prepare for.
The reason why most doctors often confuse grief for depression is because of the symptoms that are very much alike. The patient suffering from depression often does not get enough sleep and loses their appetite, something that a patient suffering from grief also shares. However, there is one significant difference between grief and depression, and that is time.
According to the DSM-V an average human has a recovery time of nearly two weeks from grief, after which the person’s state can slowly morph into depression. After two weeks, a grieving patient should show signs of improvement. If the patient doesn’t then it is possible that the patient is slowly going into clinical depression, which is very common after two weeks of grief.
Another main difference between depression and grief is the feelings of the patient at the time. During grief, the patient feels fatigue, despair, and minor feelings of guilt. Whereas in the case of depression the patient feels massive exaggerated guilt, worthlessness, and helplessness, all of which are extreme versions of the feelings mentioned above. This reason is why people who are in grief cannot be categorized as depressed during the initial stages of grief. The symptoms of grief and depression overlap, hence, making distinguishing the two very hard.

Changes in Life
Sometimes changes in life that you plan for or expect don’t go the way you want.
“Changes in life” is an inclusive term that mostly engulfs the causes mentioned above as well as a few new ones. During life, specific changes happen which can cause people to fall into depression. From changes in diet to an injury that has left you crippled, all of these things can very likely affect your emotional state and mental state. An adverse event or a series of unfortunate events can also lead to depression, whether it be spontaneously or after a certain period.
Traumatic events in one’s life are often a significant cause of depression and mostly consist of accidents or natural disasters. These events can lead to psychological and emotional trauma, something that can later transform into PTSD, which is one of the worst forms of anxiety.
While not every traumatic event may be a natural disaster or an accident, a traumatic event is an event which you have no control over. These problems can stem from places such as work, school, or even home.
Another sort of life change is one that happens voluntarily. Sometimes changes in life that you plan for or expect don’t go the way you want. This uncertainty can also lead to depression. Scenarios such as relocating, becoming a parent, retiring from a job, or the responsibilities that come with these changes can all add to your depression. The guilt and self-loathing that comes with this event are much greater than that of traumatic events. These are changes that you make. Hence, you only have yourself to blame.
Major life changes don’t always lead to a negative change in behavior or mental stability but they can. People suffering from traumatic changes or other major events in their life often don’t find help for their deteriorating health. This hesitation makes things a lot more difficult to handle. Significant life changes can also be because of a diet that you aren’t following. Alternatively, you may be dealing with the loss of a loved one. However, these traumatic incidents do not always cause depression. Instead, they cause grief to the patient, often mistaken as depression.
Symptoms
Although classic signs of depression vary from person to person, some common symptoms indicate that a person may be suffering from this disorder. Experiencing troubling symptoms for a brief period is ok. But the longer they last, the more likely depression is the culprit and the harder it is to get out of it.
Common Symptoms of Depression
- Trouble concentrating and remembering things
- Making decisions
- Weight and appetite changes
- Significant weight gain or weight loss
- Loss of interest in your daily activities including social activities and pastimes
- Feelings of hopelessness and helplessness
- Insomnia or sleep changes
- Feeling fatigued or sluggish
- Body feels heavy
- Irritability or anger
- Self-loathing
- Reckless behavior
- Unexplained pains and aches
- Back pain, stomach pain or aching muscles
Depression in Men
Men are less adept at recognizing symptoms than women. This is because men are more likely to deny their emotional needs and may hide from others to mask their true feelings. Although a large population of men experience classic symptoms such as loss of interest in hobbies and work or sleep and weight disturbances they often treat symptoms with substance abuse and channel these through anger and agitation.
Here are a few of the most overlooked signs of depression in men:
- Reckless behavior
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Back pain and headaches
- Anger
- Sleeping too little or too much
- Digestive disorders and chronic pain

Depressed men are likely to exhibit risky or callous behavior such as driving recklessly, taking up dangerous sports or practicing unsafe sex. They can become addicted to gambling and substance or alcohol abuse.
Men also exhibit unusual behavior such as becoming irritable and more sensitive to criticism. However, depression in men is also linked with a few complaints of backaches, headaches and sleep disorders. If you frequently experience sleep and digestion problems that don’t respond well to treatment, it could be due to depression.
Pay close attention to your symptoms. Waking up every night at the same time or experiencing frequent bouts of insomnia may mean you are having a tough time dealing with depression. But some men wake up feeling tired even after sleeping for 10-12 hours.
Depression in Women
Since depression usually lasts for longer periods, mood swings and changes in eating or sleeping pattern lead to a few disorders in women. Feeling sad or low for no reason is common among women who are experiencing mild or severe symptoms of depression.
Mood disorders can disrupt any woman’s daily life. The sad part is they are not easy to identify or treat. Most women don’t even recognize their symptoms and seek no help to treat their anxiety and depression. Some research reveals that women are twice as likely to develop depression as men.
Women experience depression differently than men. This is why depressed women act and behave differently from their male counterparts.
These common symptoms identify female depression:
- Losing appetite or weight
- Feeling hopeless
- Having trouble concentrating and focusing
- Feeling exhausted and weak all the time
- Feeling less important or inadequate
- Experiencing feelings of guilt
- Having thoughts about accidental death
- Feeling irritable or anxious
- Crying without any reason
- Experiencing mood swings
- Changes in sleep patterns
Unfortunately, female depression follows a distinct pattern which is (usually) not the case with most men. Hormones, menopause and other triggers also affect this pattern. Teenage girls may also experience bulimia or fall victim to anorexia nervosa if they are unable to manage their depression symptoms.

Some research reveals that women are twice as likely to develop depression as men.
Both men and women may have a low libido or experience trouble expressing their affection when depressed. That’s why it is important for both men and women to seek depression help solutions to manage their symptoms.
What It Means To Be Emotionally Numb
Almost everyone has gone through this sensation, at least one in a lifetime. This strong emotion hits during or after a stressful event. When you feel as if you are temporarily disconnected from your body and the outside world, you experience feelings of numbness and emptiness.
Much debate revolves around the subject of emotional numbness. The symptoms are commonly present as guilt, poor sleep or appetite and an inability to enjoy daily routine activities.
Some people feel numb because of anxiety. Patients describe this feeling as being in a fog, where they can’t comprehend or respond to a situation. For instance, you have to speak at an important event, but during the presentation, you go numb and feel trapped in the sense of helplessness and hopelessness.
Depression also manifests in different ways. Emotional numbness is just one of them. This feeling stems from several sources and sometimes attacks a man or a woman without any logical explanation.
However, it is crucial to find private counseling for depression that helps you stay positive to overcome the feelings of being emotionally numb. While you feel as if it might never go away, it is easier to overpower it with behavioral therapy and counseling.
If you think you are experiencing symptoms of emotional numbness, you may be:
- Losing interest in your daily activities
- Experiencing changes in sleep, appetite or feelings
- Lack of motivation
- Having trouble expressing yourself
- Experiencing memory loss
- Feeling as if your surroundings are not real
- Experiencing recurrent flashbacks to a traumatic event
- Feeling disconnected from your home or work environment
Some of the best ways you can overpower this feeling are to get more connected to the real world. Texting and social media are great ways to be in touch with your friends and loved ones. However, nothing beats in-person quality time. Spend more time with your family and rekindle old friendships to create a sense of belonging.
Suicide Ideation
This refers to having suicidal thoughts or making plans to take one’s own life. Suicide ideation can range from a brief consideration to weaving a detailed plan to try out different methods of suicide. However, it does not include the act of suicide.
Experiencing suicidal thoughts is relatively common among depressed individuals. Whether you’ve flunked an exam or lost your job, feeling depressed for prolonged times can lead you to consider suicide to end your miseries.
Although these feelings and thoughts can be temporary in most cases, some depressed men or women can become fixated on the idea.
Adults, teens, and even kids can experience suicidal thoughts, and it is essential to seek immediate help before things can take an ugly turn.
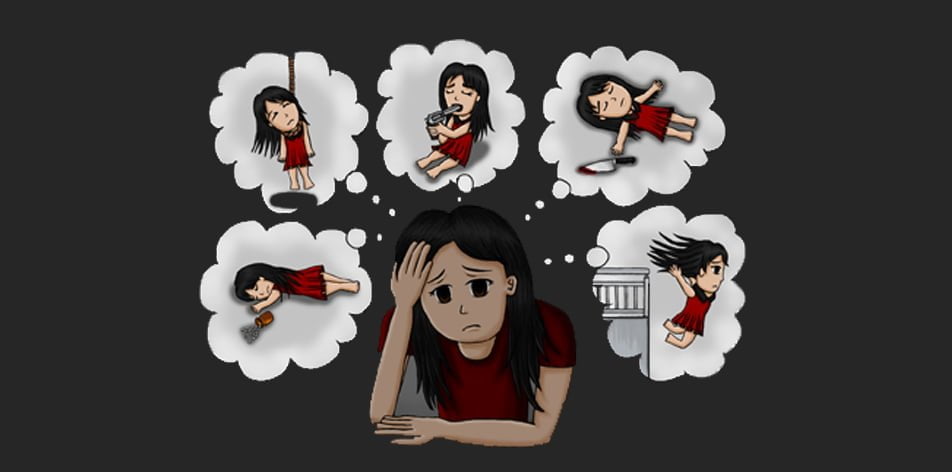

Fast Facts about Suicide Ideation
- Depression, eating disorders, substance abuse, and anxiety can lead to suicide ideation
- People who think about committing suicide all the time are less likely to execute their plans
- Hereditary genes also play a crucial role in pushing a depressed individual to go through suicide ideation
If you or someone you know shows frequent swings in mood, sleep and eating patterns, seek immediate help. Being aggressive, anxious, sad or angry all the time indicate that there is something wrong deep inside.
It is interesting to note that some people forget the idea once they update their will, give away stuff and even write a suicide note. Depressed individuals who sleep a lot more or a lot less, avoid close friends, disconnect all social connections are more at risk of experiencing suicidal thoughts.

Depression Vs. Sadness
Sadness
Sadness is a normal human emotion. It is ok to feel sad for a couple of hours or even a day. But, some people can be sown with sadness for weeks.
Many triggers induce this feeling. It could be due to the loss of a loved one or your job. The truth is, even minor events such as missing your favorite show can make you feel sad.
Here are a few common triggers:
- A recent divorce
- Loss of income or a job
- Social anxiety
- Losing a loved one
- Issues at work or home
- Failing an exam
But sadness is different from depression as a sad individual can easily vent out sadness. You can find relief by talking to a friend, crying or finding a solution to the problem.
Since sadness is linked to a trigger, taking care of the trigger helps you to overcome feelings of sadness. Most patients report that sadness recedes like the tide, once they can fix the triggers.
Depression
Unlike sadness, depression refers to an abnormal and severe emotional state. It is a kind of mental illness that overshadows our entire personality. Depression hits our behavioral and thinking patterns and also harms our physical well-being.
There are specific triggers or events to cause depression. Psychologists believe depression generally arises where there are no obvious triggers.
This is why many Hollywood celebrities and musicians suffer from this plague. Their life may seem perfect to the outside world, but only they know how awful they feel inside.
People who lead perfectly normal and happy lives are prone to undergo manic depression, even during their most successful years.
Depression scars every aspect of our lives. You no longer enjoy the things you loved once, and nothing seems to bring any happiness to you. This happens because long-term depression sucks the energy out of the patient leaving him/her less motivated to accomplish trivial or significant tasks. You stop taking pleasure in your daily routine life and contemplate suicide to get out of the mess.
Depression hits our behavioral and thinking patterns and also harms our physical well-being.
It is important that patients seek immediate counseling and help to overcome depression. It is a mental disorder that taints your perceptions and damages your self-confidence.
The scary part is that it can hit people of all ages. Although it is more prevalent in females, men are also at risk of being seriously affected by this brutal mental disorder.
It was reported in 2015, that roughly 16.1 million people (aged 18 or above) were affected by depression in the U.S. alone.
Common symptoms to look out for in both the genders include:
- Hopelessness
- Feelings of discouragement and sadness
- A loss of interest
- Zero motivation
How to Differentiate Between Sadness and Depression
Sadness
- Sadness comes and goes
- It is just an emotion
- Can last up to days or weeks
- Leads to unhappy thoughts
- Sadness is manageable
- It makes you feel low
- Sadness has a reason
Depression
- It is a chronic and consistent feeling
- Depression is physical and mental
- Depression can last for months or years if not treated
- Capable of leading to negative and suicidal thoughts
- Depressed individuals feel helpless
- You can’t even leave the house
- In some cases, there are no logical explanations

Depressed individuals also find it hard to express their feelings. Negative thoughts and overpowering feelings make it difficult for depressed people to talk it out with others. Affected individuals should seek counseling sessions for depression which can help them overcome negative emotions.
Another way to beat depression is to stay active. It is widespread for inactive people to feel worse since they are doing less. Many behavioral strategies encourage patients to identify their symptoms and know whether they are truly depressed or are just sad. Depression counseling techniques can encourage patients to participate in sports and fitness programs to beat depression the natural way.
Basic relevant behavioral strategies include but not limited to goal planning, problem-solving, social skills training, and activity scheduling. Once acquired, these behavioral styles can be applied throughout life, minimizing recurrence or relapse of depression.
Alcohol and Depression - Self Medicating
When we probe deeper into the subject, we observe that self-medicating with alcohol is a common practice for depressed individuals. It is believed that roughly 37% of people with alcohol dependence suffer from depression or anxiety. Although, it seems the perfect solution to some, in reality, alcohol and substance abuse can wreak havoc on your physical and emotional health.
We know that depression is a devastating mental disorder. It causes severe damage to your mental and physical health. From social pressures to a strong desire to escape reality, there are many reasons to turn to alcohol.
Not only alcohol forgets you trauma and reality, but it also eases physical discomfort and pain. The term self-medicating is used to describe turning to drugs or alcohol to mask the symptoms of a health issue.
But relying on alcohol has its downsides. Not only it interferes with your daily activities, but it also causes severe damage to your liver. As soon as the intoxicating effect wears off, depression hits back with a vengeance.
Becoming Dependent on Alcohol
Prolonged self-medicating also worsens your anxiety and sleep disorders.

Alcohol can make you feel better for a brief period. That’s why it is tempting to turn to alcohol for coping up with life and forgetting about what troubles your mind. It is easy to slip into drinking easily, but the benefits soon wear off, and you are back to square one.
Here are a few downsides of self-medicating using alcohol:
- You wake up feeling nervous and have shaky hands
- You start to drink more often
- Your work-life balance suffers
- You begin to binge-drink
- Other things seem less important
Prolonged self-medicating also worsens your anxiety and sleep disorders. It is only a temporary solution which everyone should avoid to lead a happier life. Your emotional state deteriorates as arguments with friends and family become part of your everyday life. Moreover, heavy drinking kills brain cells and hurts our mental health. There is always an option for free phone counseling for depression, so you don’t give in to alcohol cravings to manage symptoms of depression.
Treatment
Depression is like a hollow sphere that seems to have a never-ending dark shadow. You may feel helpless and despaired when depression surrounds you and keeps you from living a healthy and contented life. However, no matter if your depression is severe, it is treatable.
If you feel your depression is overcoming you, you should not hesitate to discuss it with a therapist. Learning about the treatment options helps you decide on the right approach you should take. Thus, you can effectively treat your depressive disorder.
From medication and therapies to healthy lifestyles, there are a plethora of effective treatments available that are helpful to overcome depression and regain a happy and hopeful life.
Treatment Options
Knowing the right treatment options is essential. The treatments options depend on the severity of your depression. Consulting a certified psychiatrist will help you determine that severity, plus, provide help if you are dealing with depression.
Effective and accessible… online therapy… works better than antidepressant pills
Online Therapy for Depression
With depression and anxiety becoming a common thing in our society, seeking professional help or therapy for depression has become essential. Fortunately, several mental health centers provide psychological counseling for depression in the different parts of the world.
The good news is that there is no need to be physically present in these centers as they provide depression counseling online. Effective and accessible, these online therapy centers work better than anti-depressant pills. Plus, there is no doubt that depression counseling is one of the ultimate treatments that can help you deal with depressive disorders in the long run.
There is a myriad of mental health care hospitals providing free counseling for depression and anxiety via their online sessions. From self-counseling for depression to online chat depression counseling, these mental institutions are of great help to the patients.
Benefits of Online Therapy
Convenient and Accessible
This is what makes online therapy an effective and way to deal with depression. No matter whether you live in the same vicinity as the mental institute or somewhere else, you can conveniently undergo online depression therapy.
Nor you have to miss any critical business trip neither has to take a day off; you can see your therapist from any location. All you need to do is to schedule a fixed time that suits both you and your therapist and attend your online therapy.
Access and Choose the Psychiatrist You Want
If you live in an area where accessing a good psychiatrist or therapist is difficult, online therapy makes it hassle-free and effortless. You can choose a therapist online, contact him/her and participate in online depression chat counseling.

Treatment Options
[A] combination of psychotherapy and medication can have a significant impact on chronic and severe depression
eTherapyPro
eTherapyPro offers a free week trial of an online therapy program to help patients manage, monitor and improve their mental health. The interactive sessions with licensed counselors are a part of an online therapy that commonly uses cognitive behavioral therapy to treat depression.The effective program provides counseling and teaches patients effective techniques to improve mental health.
Medication
Medication is one of the effective treatments for the ones suffering from depression. After examining your symptoms, the psychiatrist prescribes you certain medications to relieve depression symptoms.
On the other hand, if your depression symptoms are severe, you may require to get admitted to the hospital. Staying in the hospital is essential to get inpatient counseling for depression.
There are numerous antidepressants that your mental health doctor may prescribe you. These include:
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Selective)
Many therapists start the treatment with these medicines as they are not only safe but generally have fewer adverse side effects as compared to other antidepressants. The significant components of SSRIs are:
- Fluoxetine (prozac)
- Sertraline (zoloft)
- Citalopram (celexa)
- Paroxetine
- Vilazodone (viibryd)
- Escitalopram (lexapro)
Atypical Antidepressants
These medications do not compartmentalize into other categories of antidepressants. They are used to treat severe symptoms of depression. The major medications in this category are:
- Mirtazapine (remeron)
- Bupropion
- Nefazodone
Tricyclic Antidepressant
These medications are also for treating severe symptoms and may have side effects than any newer antidepressants. Tricyclic antidepressants are very effective but are only prescribed when you have tried SSRI doze and experienced no improvement. The major ones include:
- Imipramine (tofranil)
- Amitriptyline
- Desipramine (norpramin)
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
MAOIs are also a high level of antidepressant and prescribed only when other drugs fail to improve patient’s condition. Not only do these drugs have severe side effects but also require a good diet plan to work. The chemical formula of MOAIs can have a dangerous interaction with the specific type of foods, especially, pickles, cheese, and wines. Plus, the patients are not allowed to use any herbal supplements if they are on MOAIs.
Other Antidepressants
As mentioned earlier, treatment based on medication depends on the severity of your depression level. Considering this, your doctor may add to an antidepressant to improve effects. You can get a combination of two antidepressants, such as antipsychotics and mood stabilizers. Stimulant drugs and anti-anxiety medications may also be added for swift results.
Effective Psychotherapies for Depression
The combination of psychotherapy and medication can have a significant impact on chronic and severe depression. Here we have enlisted two effective psychotherapies that can help depression patients.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
ECT is one of the effective therapies for patients not responding to medication or drugs. The treatment is also beneficial for suicidal and psychotic patients. Moreover, ECT is more rapid and effective than drug treatments. Patients can see the results within one week after commencing the therapy.
These are the common indications to opt for ECT:
- Patient preference
- Suicide risk
- Failure of medications and drug therapies
- Increased risk of mortality and medical morbidity
- If the patient has a fruitful history of ECT

Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy includes two treatments – interpersonal therapy, and cognitive therapies. Both are associated with improved results in depression and anxiety patients.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
CBT primarily deals with depressive disorders and solve them through individual counseling. It helps patients identify their maladaptive thinking. It focuses on improving their self-esteem and develops confidence in them. Moreover, this therapy is suitable for all age groups. Hence, it solves the individual’s issues through private counseling sessions.
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
It is a time-limited therapy and caters to patients with major depression issues. It helps reduce depressive symptoms in patients to improve their interpersonal relationships and life quality.

How to Help Someone with Depression
There is no denying that depression can be insidious not only for a person but the people associated with him/her. Hence, he or she can feel frustrated, isolated and confused. A person who suffers from depression often feels distraught and adopts a silent approach.
If you see any of your loved one struggling with all these symptoms, do not wait or hesitate to help him or her. It is not less than saving a life.
Following are the few options you can mull over to help someone suffering from depression.
Make Him/ Her Feel Your Presence
The feeling of ‘Someone is there for me’ is priceless; hence this is what a depressed soul needs the most. Make him/her feel that you are always there to support. Give him/her a chance to speak, or cry whenever he/she needs it. Your support will work as the healing therapy to help your loved one regain the self-confidence.
Do Not Criticize
Remember, your words can influence your loved once and leave a powerful impact on him/her. Avoid criticizing their behavior, perspective and the way they handle things in their life. Moreover, your harsh words can be insensitive for the struggling souls, pushing them towards isolation.
Educate Yourself about Depression
This is important as you can help one suffering from depression in a better way if you know the depression symptoms, causes, and techniques to help them. Educate yourself as much as you can and understand different types of depression to offer better support.
Traveling With Depression
If you are a patient with anxiety or depression, it does not mean that you cannot travel. However, you need to be little more cautious to ensure that your journey goes smooth. The following tips may be helpful:
- Assess yourself whether you are ready to travel or not before reserving your flight. Make sure your depressive disorder is under control. Typically, you need to see if there were any flares up or medication changes within the last two-three
- Discuss your traveling plan with your therapist to know your mental fitness level.
- Make sure to explore all your mental health options at the destination you are leaving for. Search about the psychiatric facilities and mental health centers there to get immediate assistance (in case you need it).
- Always have a contingency plan; what will you do if depression strikes during your trip. Figure out the best possible way to get connected with your therapist, or finding a local mental health professional who speaks the same language.
- Make sure to carry an extra quantity of your antidepressant (in case you extend your trip days). Always pack them in your hand carry instead of a checked bag.
For those who can afford it, traveling can be a relaxing experience that promotes cognitive betterment and healing. Although depression rarely stems because the individual has yet to experience a change in scenery, being caught up in a mundane routine and work schedule can definitely make things worse. Traveling can give an individual a sense of purpose and a short-term goal i.e. having a good time that they can work towards.
Nonetheless, it still doesn’t discount the fact that one can suffer from depressive symptoms during the trip as well, which can make it difficult to focus on the current situation. In such a situation, practicing certain grounding techniques and remembering the aforementioned tips can help you make the most of your trip.
Conclusion
A depressive disorder can be immensely difficult to deal with and in most cases not knowing about the symptoms you’re facing can make it worse. Mental health awareness is crucial in this regard, whether or not you feel like you’re suffering from a depressive disorder, someone else might be and it’s important that you understand it to help the people in your life.
Whether you want to understand depressive disorders, symptoms, causes, and medications, reading up can give you a much better view on how you can improve the lives of those around you, and be more thoughtful about people who may be dealing with depression.